What do Reddit, Discord, Medium, and LinkedIn have in common? They all use what’s called a skeleton loading screen for their applications.
A skeleton screen is essentially a wireframe placeholder that appears while the application content is loading.
This placeholder mimics the layout of the actual content, letting users know that the page is in the process of loading.

The skeleton loading screen mimics the original layout, providing a visual cue that the content is on its way.
This gives the user the impression that the application is booting up and the content is loading, creating a more seamless experience.
What Is a Skeleton Loading Screen?
A skeleton screen is a version of the user interface that simulates the page’s layout as content loads. It serves as a visual placeholder that closely resembles the final content structure, keeping the user engaged during the loading process.
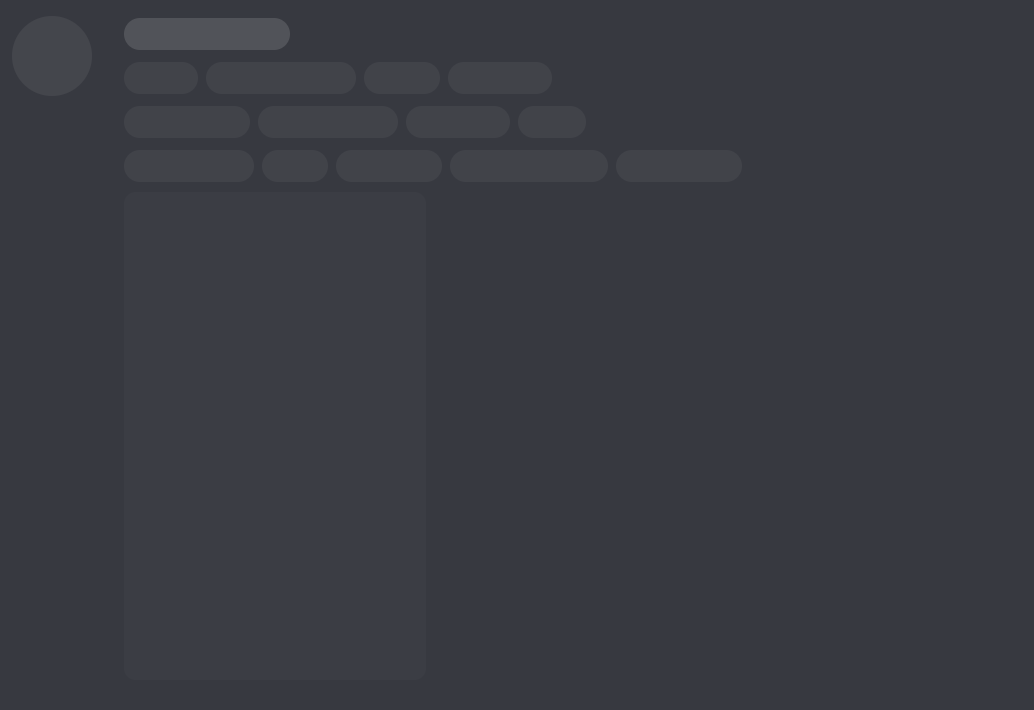
Why Use a Skeleton Loading Screen?
-
Faster Appearance: Skeleton screens create the illusion that the page is loading faster by displaying a placeholder layout immediately. Users can see the structure of the content as soon as they navigate to the page, which feels quicker and more responsive than a simple loading spinner.
-
Content Awareness: Unlike spinners, which provide no context, skeleton screens show a preview of where and what kind of content will appear. This reduces user uncertainty about what is happening and reassures them that progress is being made.
By adopting skeleton loading screens, you can make your application feel more performant and responsive, ultimately enhancing the overall user experience.
Instead of leaving users staring at a blank page or a spinner, skeleton screens keep them informed and engaged while content is loading.
How To Use Skeleton Loading with React
Setting up skeleton loading in your React project is straightforward. You can install the react-loading-skeleton package using either npm or Yarn.
yarn add react-loading-skeletonThe <Skeleton> component is designed to be used directly in your components, replacing the content while it’s still loading.
Instead of manually crafting a skeleton screen to match your content’s font-size, line-height, or margins, the <Skeleton> component will automatically fill the correct dimensions for you.
Blog Post React Component
Let’s create a basic blog post that accepts the title, subtitle, and body of text as props.
import React from "react";import Skeleton from "react-loading-skeleton";
export default function BlogPost({ title, body, subTitle }) { return ( <div> <h1>{title || <Skeleton />}</h1> <h2>{subTitle || <Skeleton />}</h2>
<p>{body || <Skeleton count={6} />}</p>
<button> {body ? "Read more" : <Skeleton height={25} width={100} />} </button> </div> );}Instead of just passing the props to the component, we’re going to use the || operator. This operator acts like an or check.
If there’s no title, (1) show the skeleton loader. If there’s a title, (2) show the title instead.
Remember, the <Skeleton> the component is designed to be used directly in your components, in place of content while it’s still loading.